In the vast expanse of renewable energy sources, wind energy stands tall, quite literally, as an emblem of sustainable power generation. The gentle sweep of the breeze, once merely admired for its cooling effect or the rustle it imparts to leaves, has now evolved into a potent force for electricity generation. In this article, we will unravel the intricacies of wind energy, from its humble origins to the colossal turbines that now dot landscapes across the globe.
What is Wind Energy?
Wind energy, also known as eolic energy, is derived from the kinetic energy of the wind. It traces its roots to ancient times when windmills were first utilised for tasks such as grinding grains or pumping water. Today, wind energy has metamorphosed into a sophisticated and essential component of the global energy matrix.
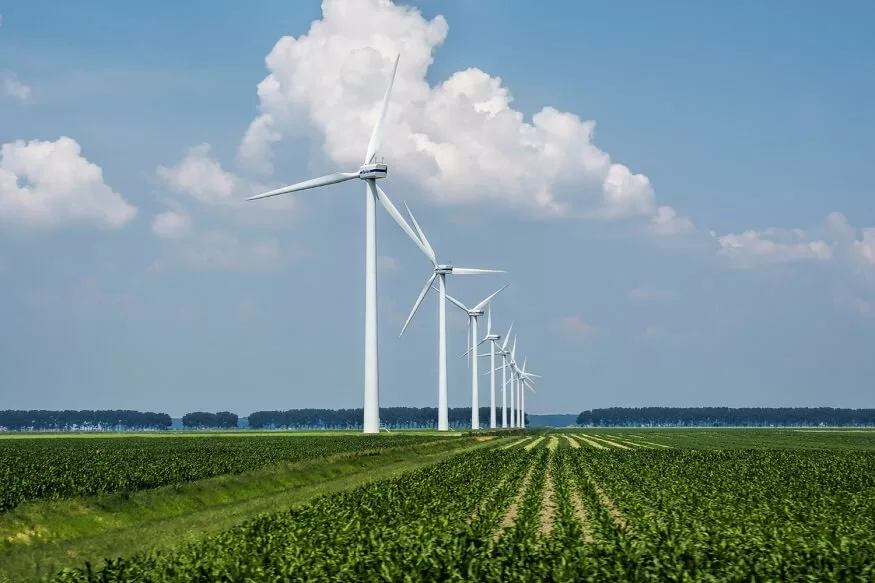
The primary mechanism involves converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical power through the use of wind turbines. These turbines consist of blades connected to a central hub, and as the wind blows, the blades rotate, driving a generator to produce electricity. The process is elegantly simple, yet the impact is far-reaching.
How is Wind Energy Used?
- Onshore Wind Farms
- Offshore Wind Farms
- Distributed Wind Power
Onshore wind farms, with their towering turbines dominating landscapes, are a common sight in many regions. These turbines are strategically placed in areas with consistent and strong winds. As the wind blows, it propels the turbine blades, converting the energy into electricity. Onshore wind farms have become a cornerstone of sustainable energy production, providing a substantial share of electricity in numerous countries.
While onshore wind farms have their advantages, offshore wind farms are gaining traction due to their potential for higher energy yields. Positioned in bodies of water, these turbines harness the often stronger and more consistent winds found at sea. Though more expensive to install and maintain, offshore wind farms offer a more visually unobtrusive option and often face less community opposition.
In addition to large-scale wind farms, there is a growing trend towards smaller, distributed wind power. This involves installing smaller wind turbines on individual homes, businesses, or community sites. While these turbines may not generate as much power as their larger counterparts, they contribute to localised energy production and can be particularly effective in rural areas.
Also Read: Who are the indigenous and tribal people?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy
Advantages of Wind Energy
- Renewable and Clean
- Abundant Resource
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Job Creation
- Energy Independence
Wind energy is an infinitely renewable resource. As long as the sun continues to shine and the Earth rotates, the wind will blow. Unlike finite fossil fuels, wind energy is inexhaustible. Furthermore, the process of converting wind into electricity produces no air or water pollution, making it one of the cleanest sources of energy.
The Earth’s surface is perpetually kissed by the wind, making it an abundant and widely distributed resource. Wind farms can be established in diverse locations, from coastal areas to mountain ridges, harnessing the power of the wind in various geographical contexts.
Wind energy boasts a low carbon footprint compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. The process of generating electricity from wind produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce overall environmental impact.
The wind energy sector has become a significant source of employment. From manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research, the industry supports a range of skilled and unskilled jobs, fostering economic growth in regions with wind energy projects.
Relying on wind energy enhances a nation’s energy security and independence. By diversifying the energy mix, countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, mitigating geopolitical and economic risks associated with fluctuations in fuel prices.
Also Read: 15 Interesting Geography Games For Kids
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
- Intermittency and Variability
- Land Use and Aesthetics
- Noise and Wildlife Concerns
- Initial Costs and Infrastructure
- Potential for Strain on Grids
A major drawback of wind energy is its intermittency and variability. The wind does not blow consistently, and energy production is contingent on wind availability. This inherent variability necessitates backup power sources or energy storage solutions to maintain a stable and reliable electricity supply.
Onshore wind farms often require large expanses of land, leading to concerns about land use and aesthetics. The visual impact of turbines on landscapes and potential disruption to local ecosystems can be contentious issues, sparking debates in communities where wind projects are proposed.
The operation of wind turbines can generate noise, which, while usually at acceptable levels, has raised concerns in some communities. Additionally, there are ongoing studies on the impact of wind farms on wildlife, particularly birds and bats, as collisions with turbine blades can pose a threat to local fauna.
While the operational costs of wind energy are relatively low, the initial investment in infrastructure can be substantial. The cost of manufacturing, transporting, and installing turbines, especially in offshore projects, can pose financial challenges, although advancements in technology are gradually reducing these costs.
Integrating a significant amount of wind energy into existing power grids poses technical challenges. The variability of wind power requires grid operators to adapt quickly to fluctuations in supply, necessitating smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions to maintain a stable and resilient power system.
Also Read: How Science Teaches Life Skills
Wind energy has emerged as a key player in the global transition towards sustainable and clean energy. The positives of wind power are evident in its renewable nature, low environmental impact, and potential job creation. However, the path is not without obstacles, as the intermittency of wind and concerns about land use and wildlife impact continue to be addressed.
As we navigate the complexities of our energy landscape, it is crucial to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy with a balanced perspective. With ongoing technological advancements, policy support, and community engagement, wind energy is poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping a greener, more sustainable future.
EuroSchool is at the forefront of innovative and comprehensive education. The curriculum goes beyond traditional methods, incorporating hands-on experiences and interactive lessons to make the learning process engaging and impactful.