The natural world functions through a delicate balance of relationships, where every organism depends on another for survival. One of the most fundamental concepts that explains this interdependence is the food chain. Understanding the food chain helps us learn how energy flows through ecosystems and why every living organism, big or small-plays an important role.
This guide explains what a food chain is, its definition, types, real-life examples, and the importance of food chains in maintaining ecological balance.
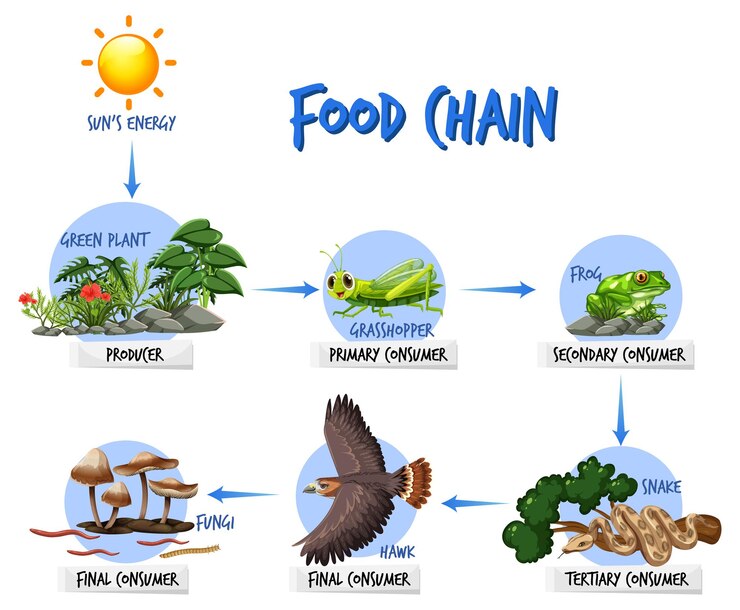
What Is a Food Chain? (Definition)
A food chain is a linear sequence that shows how energy and nutrients pass from one organism to another in an ecosystem. It begins with producers, usually green plants, and moves through different levels of consumers, ending with top predators.
Simple Food Chain Definition:
A food chain is a series of living organisms where each organism serves as food for the next one in the sequence.
This concept helps us understand energy transfer, population control, and the overall functioning of ecosystems.
Types of Food Chain
There are four major types of food chains, each playing a distinct role in nature.
1. Grazing Food Chain
Characteristics:
- Starts with green plants (producers)
- Energy flows from plants → herbivores → carnivores
- Common in grasslands, forests, and aquatic ecosystems
Example:
Grass → Deer → Lion
This is the most common and simplest type of food chain, especially in terrestrial ecosystems.
2. Detritus Food Chain
Characteristics:
- Begins with dead and decaying organic matter
- Includes decomposers like bacteria and fungi
- Essential for nutrient recycling
Example:
Dead leaves → Earthworm → Bird → Hawk
This food chain is crucial for maintaining soil fertility and ecosystem sustainability.
3. Microbial Food Chain
Characteristics:
- Driven by microorganisms
- Important in soil and aquatic ecosystems
- Helps recycle nutrients at a microscopic level
Microbial food chains play a key role in nutrient cycling and decomposition.
4. Parasitic Food Chain
Characteristics:
- Energy flows from host to parasite
- Includes parasites and hyperparasites
- Often complex and multi-layered
Example:
Tree → Bird → Parasite → Bacteria
Food Chain Examples in Different Ecosystems
Grassland Ecosystem
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Energy moves from plants to herbivores and then to higher-level carnivores.
Aquatic (Ocean) Ecosystem
Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Large Fish → Shark
This food chain highlights the importance of phytoplankton as the base of marine life.
Forest Ecosystem
Trees → Insects → Birds → Fox
Forests support diverse and interconnected food chains.
Desert Ecosystem
Cactus → Desert Mouse → Snake → Hawk
Even extreme environments maintain balanced food chains.
Arctic Ecosystem
Phytoplankton → Krill → Fish → Seal → Polar Bear
This chain shows survival and energy flow in cold climates.
Also Read: Good Habits for Students: Building the Foundation for Lifelong Success
Importance of the Food Chain
Understanding the importance of food chains is essential for environmental awareness and sustainability.
1. Energy Transfer
- Shows how energy flows from the sun to producers and then to consumers
- Explains energy loss at each trophic level
2. Nutrient Recycling
- Decomposers break down dead matter
- Nutrients return to the soil and water for reuse
3. Ecological Balance
- Controls population sizes
- Prevents overpopulation and extinction
4. Biodiversity Conservation
- Every species has a role
- Strong food chains support resilient ecosystems
5. Indicator of Ecosystem Health
- Changes in food chains signal environmental damage
- Helps scientists monitor climate and habitat changes
6. Human Survival & Resources
- Agriculture, fisheries, and food security depend on stable food chains
- Disruption directly affects human life
7. Climate Change Understanding
- Climate change alters food chains
- Helps predict the ecological impacts of global warming
Final Thoughts
The food chain is a foundational concept in environmental science that explains how life on Earth is interconnected. From tiny microorganisms to apex predators, every organism contributes to maintaining balance in nature.
At EuroSchool, students learn about food chains through interactive models, visual diagrams, experiments, and outdoor exploration, helping them understand ecology beyond textbooks. This approach is one of the reasons why CBSE schools in Electronic City Bangalore, CBSE schools in Yelahanka, and even parents comparing ICSE schools in HSR Layout consider EuroSchool as a preferred choice for holistic learning.
A strong understanding of food chains not only builds scientific knowledge but also nurtures environmentally responsible citizens.